By Alfredo Pascual
DTI Secretary

A. STI-driven Industrialization
As the country enters the post pandemic future; implementing an inclusive, sustainable, and resilient industrial policy is an imperative to build a more competitive economy.
Through science, technology, innovation (STI) and the use of essential digital technologies, industries would be in a better position to face competition in both domestic and export markets and pave the way for industrial transformation.
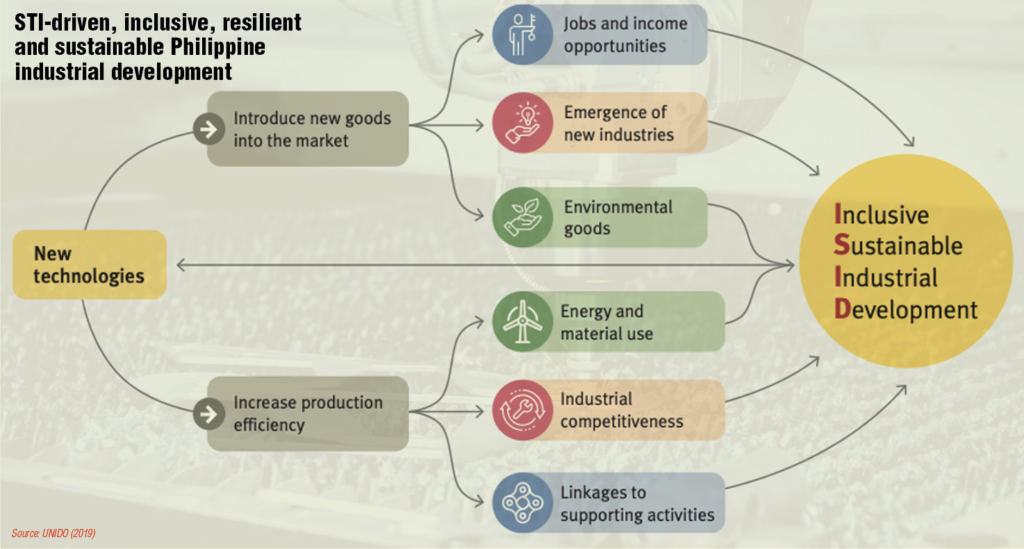
We view the adoption of new technologies as a way to strengthen innovation through the creation of new products and services in the market resulting in more quality jobs, higher incomes, emergence of new industries, and promotion of environmental goods.
Through smart manufacturing, production efficiency improves leading to more efficient energy use, industrial competitiveness, and creation of linkages to supporting industries.
The use of science, new technologies and innovation is a crucial step to upgrade our industries toward a more inclusive and sustainable industrial development. The same wave of technologies will help our industries in transitioning towards a rapid and resilient economic recovery.
.
.
What we envision is a prosperous economy driven by competition, innovation, productivity and dynamic industry ecosystems that serve as foundation for generating quality jobs and investments, creating new products and services, improving environmental sustainability, and ensuring shared prosperity for all.
The goal is to grow and develop globally competitive and innovative industries that support inclusive growth and improved environmental sustainability and quality of life for Filipinos.
B. Key Pillars
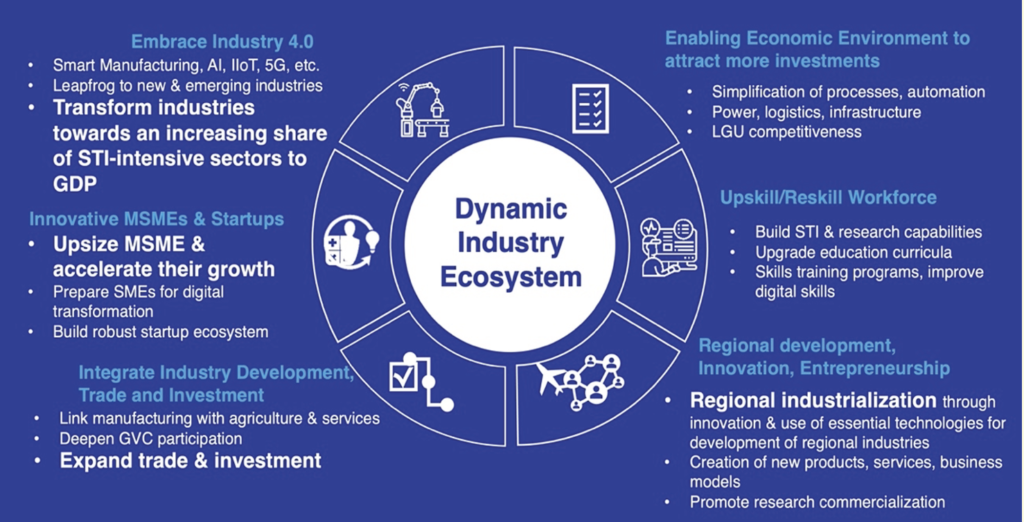
The above vision and goal are based on six major pillars and strategic actions to be pursued by DTI through a whole of government and whole of society approach and in collaboration with other government agencies, industry, academe, and other stakeholder partners:
1. Embrace Industry
4.0 Technologies
- Transform industries towards an increasing share of STI-intensive sectors to gross domestic product (GDP) through the adoption of new technologies
2. Support the digital transformation of MSMEs and the growth and development of startups
- Upsize MSMEs and accelerate their growth by enabling them to scale up from micro to small, from small to medium, and from medium to large; focus on innovation and digitalization to improve MSME productivity growth and employment creation; upgrade their participation in global value chains; enhance their digital and entrepreneurship competencies; improve their access to management and workforce skills; diversified financing instruments, technology, innovation and networks
- Build a robust startup ecosystem
3. Integrate trade, investment promotion, and industry development policies to expand and diversify trade and investment and upgrade participation in global value chains (GVC)
- Integrate our production systems by linking manufacturing, agriculture, and services; deepen GVC participation; pursue a more aggressive trade and investment policy; expand and diversify our exports, trade and investment partners
4. Develop capacity-building and human capital programs to prepare the workforce for future production
- Build science, technology and innovation (STI) capabilities through the adoption of advance digital production, investment in R&D and other innovation activities, and building new and future skills along with research capacity of the workforce to increase productivity and production efficiency
5. Promote regional industrialization through innovation and entrepreneurship
- Bridge the gaps in innovation and entrepreneurship ecosystems; develop regional industries and clusters to contribute to value creation in local and regional economies and sustain competitive advantages, upgrade regional economic activities and integrate with well-functioning and digital cities
6. Create an enabling environment to attract more investments
- Strengthening the institutional and regulatory framework to eliminate bureaucratic red tape, streamline and automate government procedures and regulations, scale up investments in digital infrastructures, and improve investments in building physical infrastructure like roads, power, logistics, water, sanitation, modern and efficient air and sea infrastructure, including education, health infrastructure, and shelter
C. Priority Clusters for Industry Development, Trade, and Investment
Manufacturing is the country’s guarantee to sustainable and inclusive growth because it provides more stable and higher paying jobs. DTI will lead in positioning the manufacturing sector for success and link it with agriculture and services especially the creative industries, R&D, IT-business process and knowledge process outsourcing, software development and the digital economy in which the country possesses strategic advantages.
Leveraging on the fourth Industrial Revolution technologies and our existing industrial strengths and competencies, we will leapfrog into new and emerging industries by
- Modernizing our manufacturing base,
- Implementing our innovation and digital transformation plans towards manufacturing, agriculture, and services development, and
- Upgrading our participation in the global technological platforms.
Given the changes in consumer trends and with the acceleration of the adoption of new technologies in the last two years of the pandemic, the following four industry clusters are seen as potential sources of growth in the country:
- Industrial, Manufacturing and Transport (IMT),
- Technology, Media and Telecommunication (TMT),
- Health and Life Science (HLS), and
- Modern Basic Needs, Resilient Economy. The first three clusters are currently undergoing global reconfiguration and provide an opportunity for the Philippines to upgrade, diversify and reposition its global value chain participation.
1) Industrial, Manufacturing and Transport
The Industrial, Manufacturing and Transport (IMT) cluster provides the country with upgrading opportunities in aerospace, automotive, and semiconductors. The Philippines already hosts the number one aircraft interiors company in the world (Collins Aerospace) and the world’s leading aircraft Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul company (Lufthansa Technik).
But there is a need to attract other suppliers and expand the cluster. As automotive companies shift to all-electric vehicles (EVs) manufacturing, the switch will be a primary change in the automotive global value chain. DTI is keen on opportunities for the country to enter the EV global value chain. The aim is to adopt relevant technologies especially for producing or developing pollution reduction and green vehicles, IT in vehicles, and precision metal components
The semiconductor industry can also benefit from the recent boost in digitalization amid the COVID-19 pandemic. Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test, or OSAT, is vulnerable to disruptive technologies.
Hence, increasing skills to undertake R&D is necessary to help improve business for OSAT firms in the country. The common thread among all these three IMT subsectors is the electronics and electrical parts and components global value chains.
.
The goal is to attract foreign direct investments to design capacity so that more value-added is captured and manufacturing is expanded in the country.
The IMT cluster covers the following: aerospace and maintenance, repair and overhaul (MRO) including flight control actuation systems, servo actuators, servo valves, galley inserts, structures and equipment, seat parts, lavatories, interior fit-out, panel assembly, electronics, airframes and sub-assemblies and MRO base and line maintenance; automotive including auto electronics, advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) components, engineering services outsourcing, electric motor powertrains like battery, Public Utility Vehicles, electric vehicles (EV) and EV parts, green metals value-adding and processing, semiconductor manufacturing services including wafer fabrication, integrated circuit design, R&D; electronic manufacturing services including aerospace electronics, consumer electronics, medical devices, telecommunications equipment, and power storage; adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies.
2) Technology, Media and Telecommunication
The Technology, Media and Telecommunication (TMT) cluster will provide the Philippines opportunities from the digitalization of services. The key trend for the BPO sector is the switch from cost saving to value addition.
The next decade will also witness the BPO segment as a cross-cutting contributor to the competitiveness and efficiency of other global value chains it supports.
That 82% of BPOs and shared services centers in the Philippines serve global markets is a positive attribute that can be leveraged to increase the country’s participation in the TMT global value chain. With the pandemic, interest in data centers has also increased globally.
The Philippines is now seen as the destination of new data centers being established worldwide. DTI and the Board of Investments have placed hyperscalers and data centers as top priorities in the investment promotion campaign, “Make It Happen in the Philippines.”
The hyperscale industry is seen as the next growth engine of the country. On the last week of July, PLDT launched its Jupiter Cable System which connects the US and Japan to the Philippines.
This will provide a vital superhighway for digital data with its capacity almost equal to the existing cables connecting the Philippines to other countries.
The TMT cluster covers the following: IT-BPM, hyperscaler data centers, creative industries, transshipment facility operations for global logistics, regional telecommunication infrastructure services, digital economy; new products, activities or solutions using digital technologies like artificial intelligence, robotics, augmented reality, virtual reality, mixed reality, 5G connectivity, and Internet of Things (IoT) in the following areas:
- Smart technology: applications in buildings, homes, factories, agriculture, cities, interconnected products and services, voice assistants embedded in TV sets, cars home appliances, smart home devices, home robots
- Resilient technology: disaster preparedness/mitigation, cyber security, renewable energy
- Vehicle technology: self-driving cars, multimodal transportation, EV
- Audio, video, education technology
- E-gaming: console and pc gaming software, mobile gaming; immersive audio and advanced communication capabilities; cloud gamingplatforms; gaming accessories
- Metaverse
3) Health and Life Science
In the Health and Life Science (HLS) cluster, the goal is to make the Philippines self-sufficient in pharmaceuticals (with companies like Lloyd Laboratories aiming to make the Philippines self-sufficient in pharmaceuticals), medical devices, healthcare services, digital health products and services such as personal health wellness technology products, therapeutic systems addressing chronic diseases, telemedicine solutions and AI assisted diagnoses.
This cluster plays a strategic security role and opens income-generating opportunities in the country.
Over the next decade, manufacturing medicines faster and cheaper will continue to be the mantra of multinational companies. The sector will also witness smaller, innovative, more agile pharmaceutical companies taking a more critical role in bringing medicines, including generic kinds, to the market.
The integration of pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and healthcare services can facilitate the emergence of an HLS cluster in the Philippines.
The HLS cluster covers the following: life sciences and biotechnology sector, vaccines, pharmaceuticals medical devices, healthcare services, digital health products and services such as personal health wellness technology products, smart watches, lighter health wearables, more precise sensors, therapeutic systems addressing chronic diseases, telemedicine solutions and AI assisted diagnoses
4) Modern Basic Needs, Resilient Economy
The Modern Basic Needs, Resilient Economy cluster refers to modern basic needs such as food, shelter, infrastructure, education along with activities that foster economic resilience.
Given the need to pursue food security and modernize our agricultural and fishing sector along with other goals such as quality education, clean water and sanitation, and affordable and clean energy; these activities offer opportunities for new investments to support the country’s economic recovery and long-term sustainable and inclusive growth.
The RBI and EGS cluster covers the following activities and sectors: food security, agro-industrial including coffee, cacao, coconut, fruits and nuts, tropical fibers, rubber and other high value crops; fishing, blue economy, processed minerals, infrastructure, education, shelter, sanitation, textile, chemicals and plastics, and sectors that foster economic resilience such as energy efficiency, renewable energy, and goods that improve the quality of life while minimizing the use of resources and inputs.
D. Planned Policies, Programs and Initiatives for Industrial Transformation and Development
In developing the above industries and activities, the following strategic policies and actions will be implemented through a whole of government and whole of society approach:
1) Embrace Industry 4.0 Technologies
- Promote industries’ shift towards digital transformation and craft and implement people-centered digital transformation plans and programs with focus on inclusive growth
a) Implement the Artificial Intelligence Roadmap through the establishment of the Center for Artificial Intelligence Research & Development.
AI adaption can enable the country to tap vast opportunities to help maintain the regional and global competitiveness of industries, prepare the future workforcefor the jobs of the future, and attract the Artificial Intelligence R&D of multinational and big tech companies to locate in the Philippines.
The Center would be a public-private partnership to serve as hub for data scientists and researchers to perform collaborative Artificial Intelligence R&D, consultancy services, create AI tech products, and conduct data literacy programs.
The Center would focus on key areas utilizing AI such as precision farming to improve the productivity of the agriculture sector and increase the incomes of farmers, smart manufacturing, healthcare services, AI-powered BPO, smart cities, resilient technology.
b) Through the Smart Industry Readiness Index (SIRI) project, support firms and industries that are shifting to new technologies by providing deeper awareness and understanding of digital transformation and assistance to firms in assessing their technology readiness and formulation of their firm-level Industry 4.0 roadmaps.
c) Build an Industry 4.0 pilot factory (I4PF) to serve as platform for a collaborative learning environment to teach and demonstrate Industry 4.0 management and production technology like robots, automation, Internet of Things, and smart factory especially to large enterprises, SMEs, researchers and universities.
Apart from the technology and learning spaces, a government Industry 4.0 sandbox equipped with advanced manufacturing modules and technology also will be built for R&D and prototyping activities.
- Design support measures like soft loans or subsidies and technical assistance programs to help firms increase resilience and become more agile in production and supply systems enabled by advanced technology and automated processes.
Ionics is a Filipino EMS company that invested in a smart factory which allowed them to operate during the pandemic. While the crisis has affected them significantly, the impact on their business would have been far much worse had it not been for their smart factory.
Union Bank (UB), the country’s first 5G-powered bank, has been delivering innovation and digital initiatives to promote financial inclusion by bringing digital financial services to unbanked and underbanked individuals in financially underserved communities.
During the pandemic, usage volumes of its platform rose by over 3000% in the last six months of 2020.
Its network also helped expedite the disbursement of the Department of Social Welfare and Development’s Social Amelioration Program.
see link for more
